基础概念 JDK、JRE关系 总: JDK包含JRE、JRE包含JVM
JDK(Java Development Kitchen):Java开发工具,包括java编译器、java虚拟机、java类库等java开发运行所需的所有东西
JRE(Java Runtime Environment):Java运行环境,包含java虚拟机JVM和java类库
JVM(Java Virtual Machine):Java虚拟机,跨平台支持基础,真正运行java程序的地方
结:
1、安装JDK即表示安装了Java开发运行所需的所有环境
2、如果是企业部署情况下,可能不需要开发环境,因此只需安装JRE能够至此java项目运行即可
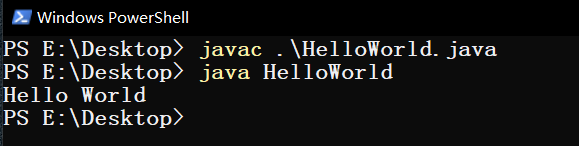
java程序运行过程 总: javac将.java文件编译成.class文件,java运行.class文件
安装好的JDK中包含一个java.exe和javac.exe,javac.exe用于将.java文件编译成跨平台的.class文件,java.exe将.class文件转换为机器码并执行。
简单的java程序,HelloWorld.java:
1 2 3 4 5 public class HelloWorld { public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World" ); } }
cmd中执行以下命令运行:
1 2 3 javac HelloWorld.java java HelloWorld > >>HelloWorld
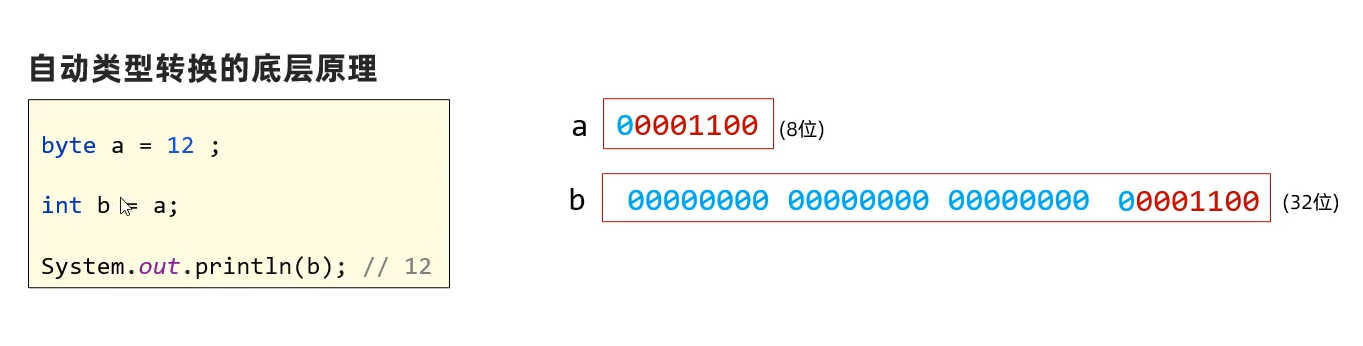
基本语法 类型转换 自动类型转换 小范围类型的变量,可以直接直接复制给大范围的变量,以下遍历自动向下转换,可跨级
byte:1字节
short:2字节、char:1字节
int:4字节
long:8字节
float:4字节
short:8字节
底层原理:小范围变量转换成2进制填到目标进制二进制后,目标进制变量前边其余位填充0
代码块:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public class Type { public static void main (String[] args) { autoTypeConversion(); autoTypeConversionInExpression(); } public static void autoTypeConversion () { System.out.println("自动类型转换输出:" ); byte a = 127 ; int b = a; float f = b; char c = 'v' ; int d = c; System.out.println("b: " + b); System.out.println("f: " + f); System.out.println("d: " + d); } public static void autoTypeConversionInExpression () { System.out.println("表达式中的自动类型转换输出:" ); byte a = 10 ; byte b = 20 ; int c = a + b; float d = a + b; System.out.printf("c: %d\nd: %s" , c, d); } }
强制类型转换 语法:数据类型 变量2 = (数据类型) 变量1
底层原理:以int -> byte为例,将int的二进制后8位,直接放在byte的8位二进制上
代码块:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public static void forceTypeConversion () { System.out.println("强制类型转换输出:" ); int a = 10 ; int b = 1000 ; byte c = (byte )a; byte d = (byte )b; System.out.printf("c: %d\nd: %s\n" , c, d); }
注意:强制;类型转换可能造成数据溢出(丢失)
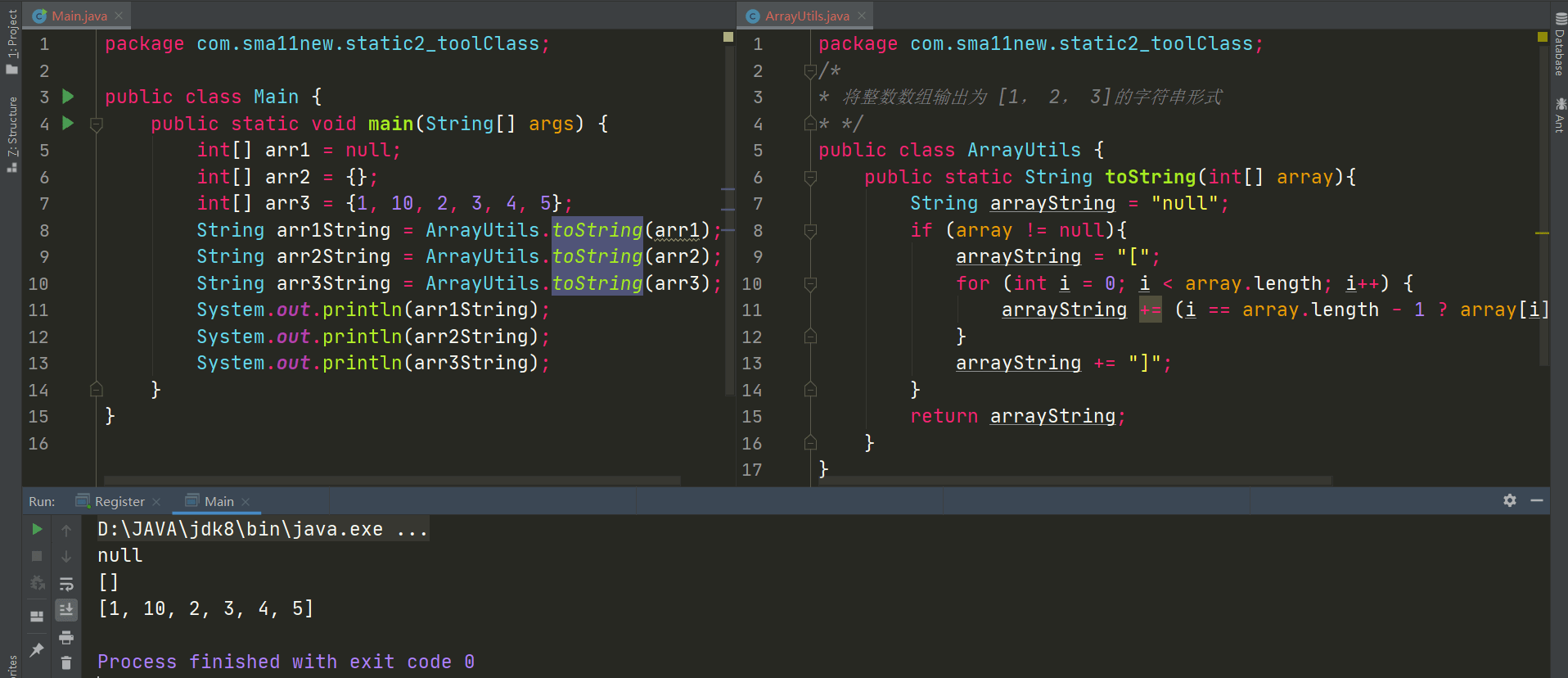
数组 静态定义 完整版:int[] a = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4};
简化版:int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4};
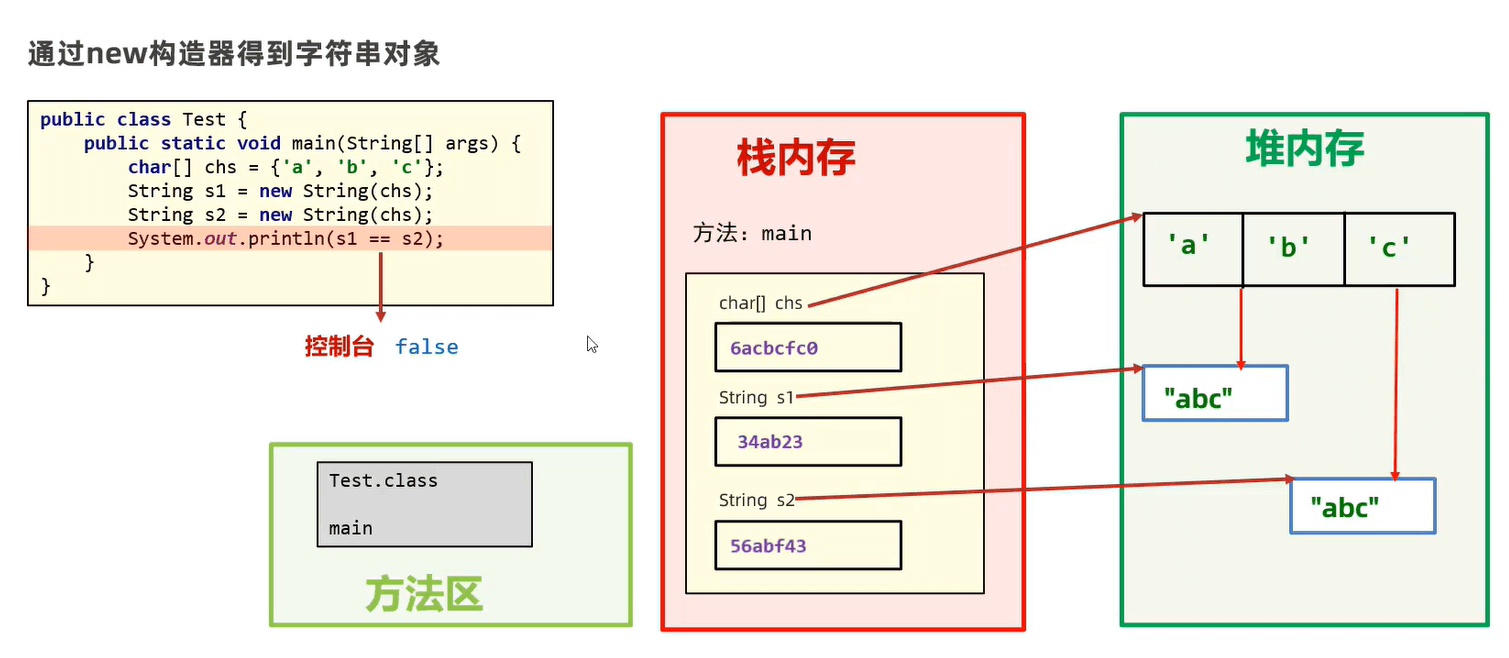
可见其实数组是一个对象。
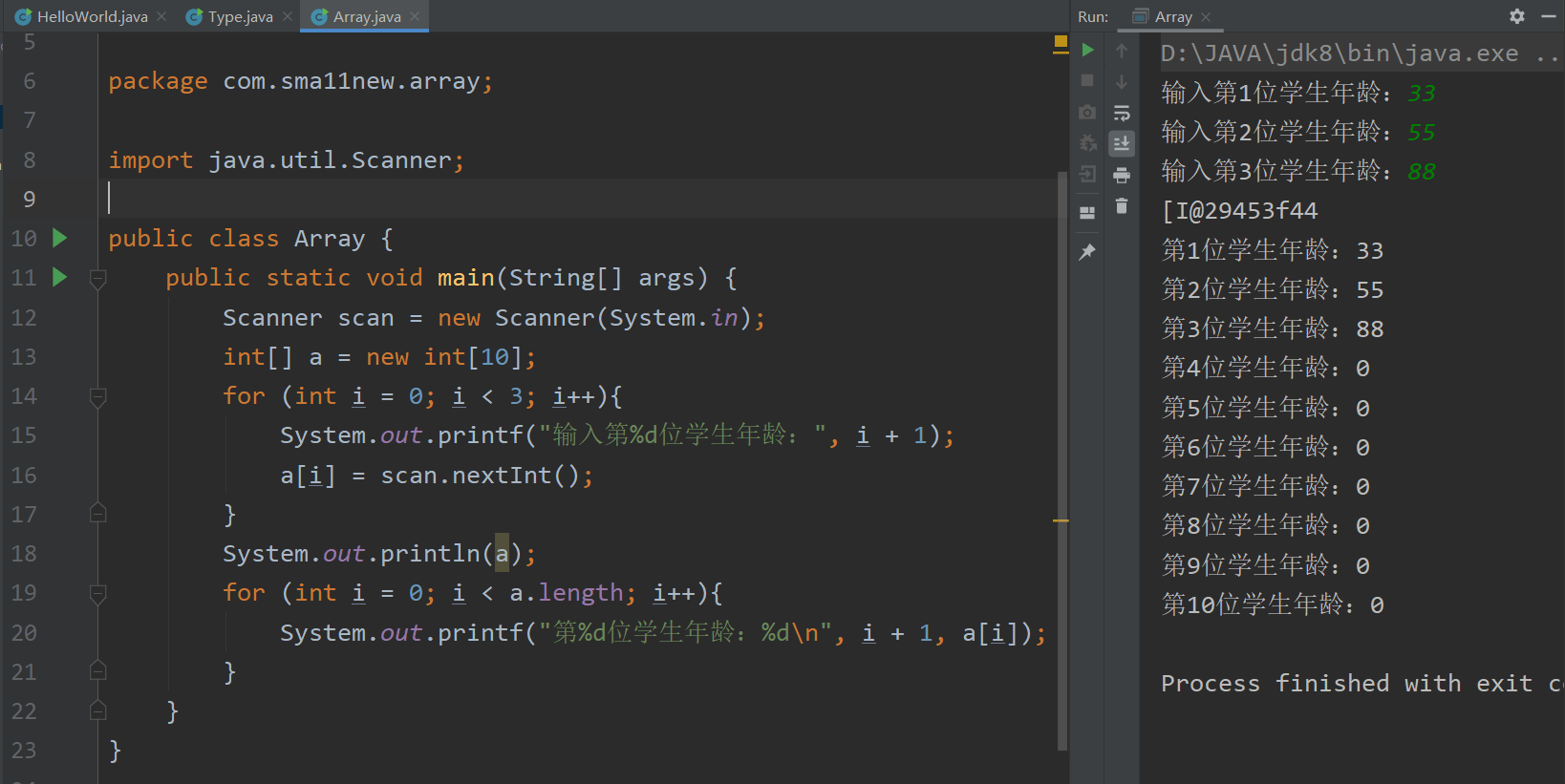
动态定义及访问 int[] a = new int[10];
访问并赋值代码块:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package com.sma11new.array;import java.util.Scanner;public class Array { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in); int [] a = new int [10 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++){ System.out.printf("输入第%d位学生年龄:" , i + 1 ); a[i] = scan.nextInt(); } System.out.println(a); for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++){ System.out.printf("第%d位学生年龄:%d\n" , i + 1 , a[i]); } } }
数组内存分配 Java内存分为以下:
栈 :方法运行时所进入的内存,变量也是存在这里 堆 :new出来的对象会存在此内存空间方法区 :字节码文件加载时进入的内存空间(class文件)本地方法栈
寄存器
定义数组变量时在堆区申请连续空间,栈区的变量存的是数组在堆区的首地址,因此多个变量接收同一数组时,接收的是数组地址。
方法重载 定义:同一类中,出现多个方法名称相同,但是参数列表不同,这些方法就是重载方法
重载方法可相互调用,代码块:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Method { public static void main (String[] args) { fire(); fire("岛国" ); fire("美利坚" , 20 ); } public static void fire () { System.out.println("默认发射1枚武器" ); } public static void fire (String location) { fire("岛国" , 1 ); } public static void fire (String location, int count) { System.out.println("向" + location + "发射" + count + "枚武器" ); } }
参数列表不同:形参的个数、顺序、类型不同,不关心形参名称。
重载方法判断:
1 2 3 4 5 public static void find () {} public static void find (int a) {} public static void find (int a, double b) {} public static void find (double b, int a) {}
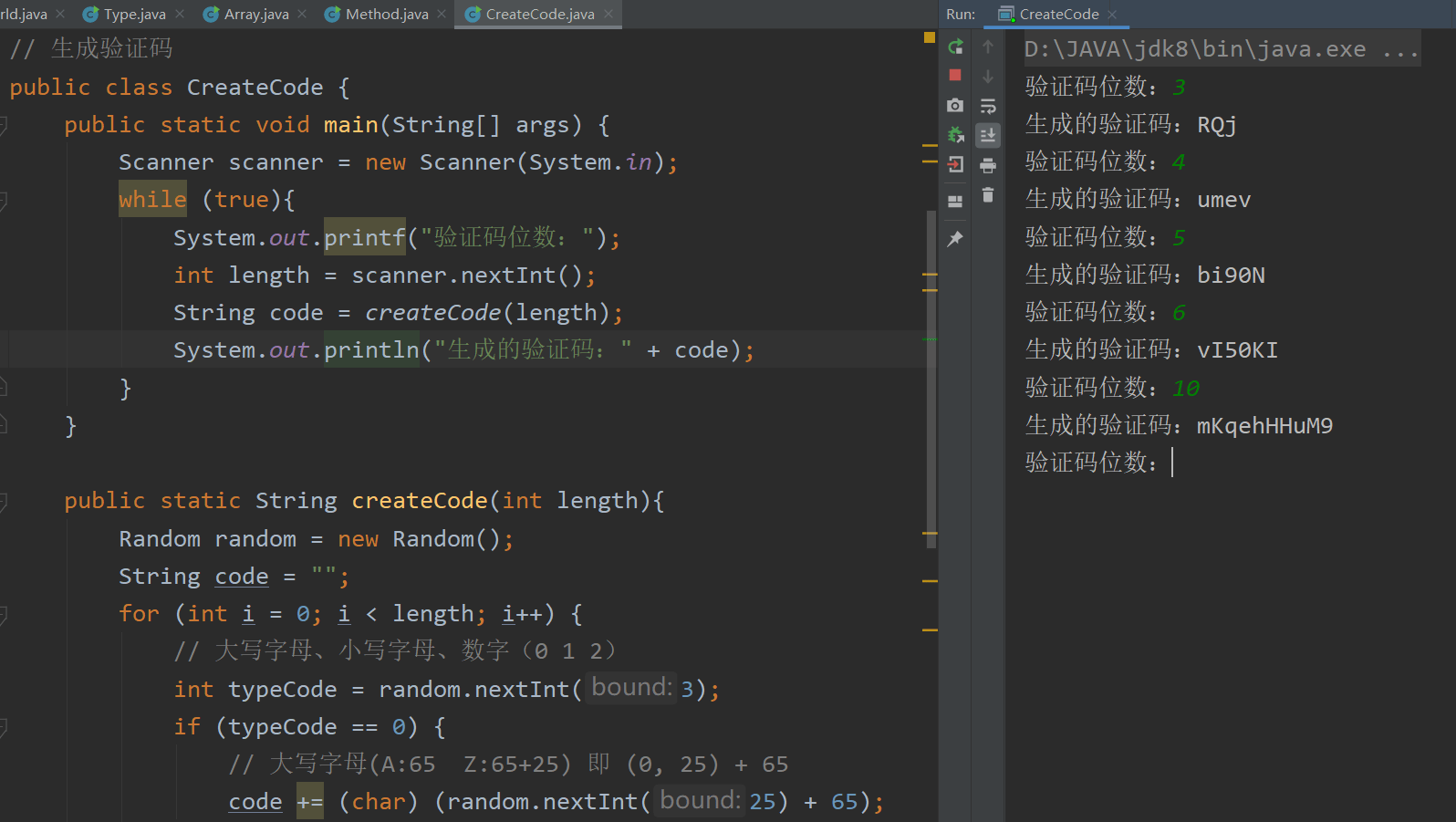
代码编写 生成验证码 CreateCode.java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 package com.sma11new.method;import java.util.Random;import java.util.Scanner;public class CreateCode { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); while (true ){ System.out.printf("验证码位数:" ); int length = scanner.nextInt(); String code = createCode(length); System.out.println("生成的验证码:" + code); } } public static String createCode (int length) { Random random = new Random (); String code = "" ; for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { int typeCode = random.nextInt(3 ); if (typeCode == 0 ) { code += (char ) (random.nextInt(25 ) + 65 ); }else if (typeCode == 1 ){ code += (char ) (random.nextInt(25 ) + 97 ); }else if (typeCode == 2 ){ code += (random.nextInt(10 )); } } return code; } }
相关知识点:
Random类和Scanner类的使用
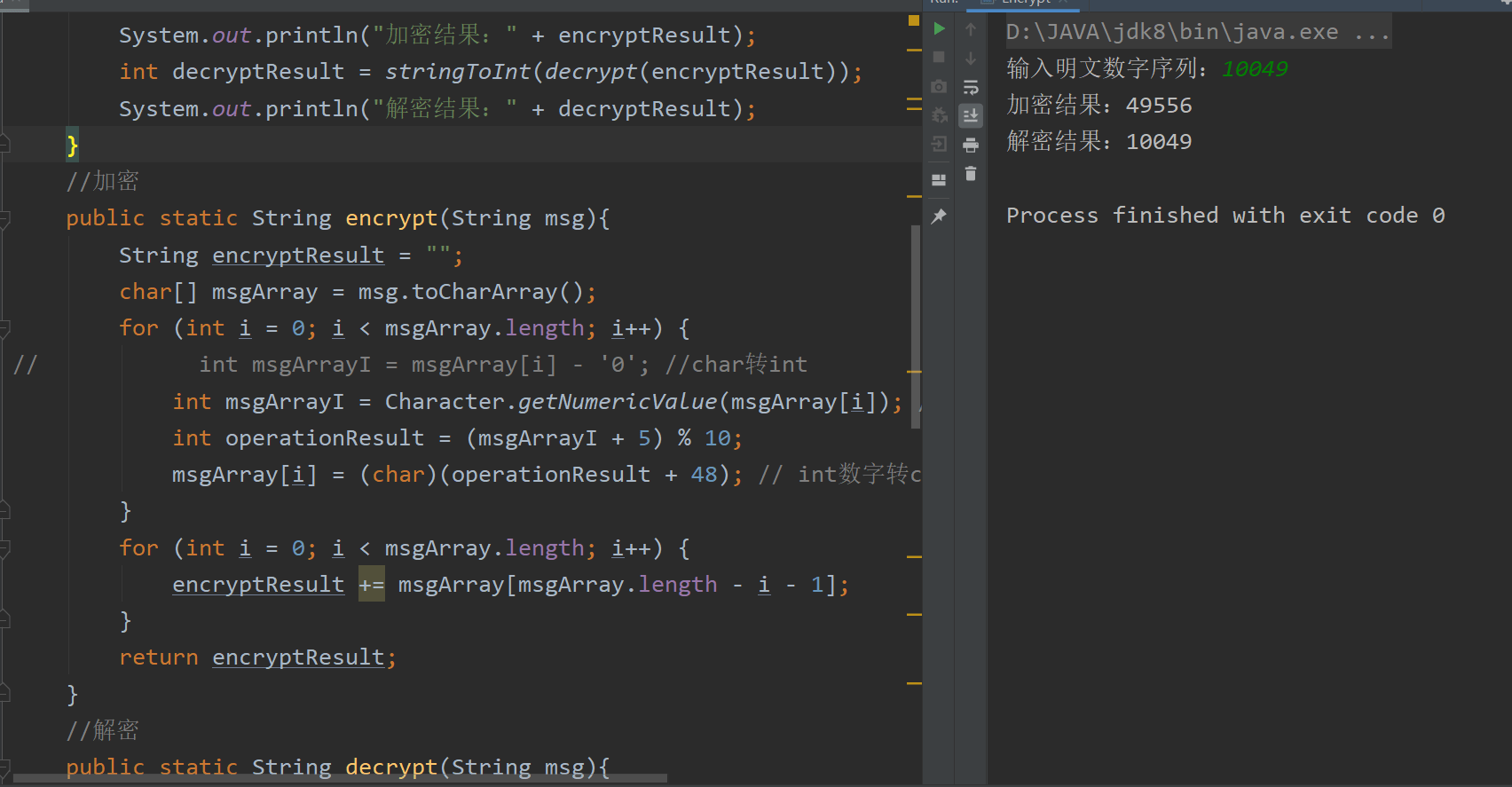
数字加解密 要求:一串数字,每位加5,取余10,再将结果反转,得到密文,并还原出明文
Encrypt.java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 package com.sma11new.method;import java.util.Scanner;public class Encrypt { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); System.out.printf("输入明文数字序列:" ); int msg = scanner.nextInt(); String encryptResult = encrypt(intToString(msg)); System.out.println("加密结果:" + encryptResult); int decryptResult = stringToInt(decrypt(encryptResult)); System.out.println("解密结果:" + decryptResult); } public static String encrypt (String msg) { String encryptResult = "" ; char [] msgArray = msg.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < msgArray.length; i++) { int msgArrayI = Character.getNumericValue(msgArray[i]); int operationResult = (msgArrayI + 5 ) % 10 ; msgArray[i] = (char )(operationResult + 48 ); } for (int i = 0 ; i < msgArray.length; i++) { encryptResult += msgArray[msgArray.length - i - 1 ]; } return encryptResult; } public static String decrypt (String msg) { String decryptResult = "" ; char [] msgArray = msg.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < msgArray.length; i++) { msgArray[i] = (Character.getNumericValue(msgArray[i]) >= 5 ) ? ((char )(Character.getNumericValue(msgArray[i]) - 5 + 48 )) : ((char )(Character.getNumericValue(msgArray[i]) + 5 + 48 )); } for (int i = 0 ; i < msgArray.length; i++) { decryptResult += msgArray[msgArray.length - i - 1 ]; } return decryptResult; } public static String intToString (int msg) { String result = "" + msg; return result; } public static int stringToInt (String msg) { int result = Integer.parseInt(msg); return result; } }
相关知识点:
char和int的相互转换
String类型转换为数组
三目运算符要在最前边写接收变量:n = (a > b) ? a : b;